MongoDB is one of the most popular NoSQL databases. It is a document-oriented platform that stores data as BSON format, which is a binary extension of JSON-like document format. Documents are grouped together into a collection. A collection in MongoDB is analogous to a table in a relational database.
MongoDB can be deployed in a variety of ways—and MongoDB provides various methods for managing backup and recovery for different deployment options. However, there are no good solutions available to consistently manage backup and recovery at scale across all the MongoDB deployment platforms.
Until now.
Rubrik backup and recovery for self-managed MongoDB deployments is an easy-to-use, feature-rich data recovery management solution. Here’s how it works.
The Anatomy of MongoDB Backup
MongoDB collections have a flexible schema design that supports nested documents, arrays, and dynamic schema to enable adaptable data modeling. MongoDB provides horizontal scalability, performance, and high availability for modern applications that require storing big data with flexible and scalable deployments.
MongoDB has the following deployment options:
- MongoDB Atlas: A fully-managed cloud DBaaS offering
- MongoDB Enterprise: A self-managed commercial offering with additional capabilities and advanced security features
- MongoDB Community: A self-managed free-to-use open-source offering
Just like any data management platform, backing up your MongoDB data protects against data loss. But unlike traditional structured databases, NoSQL databases backup and recovery is more challenging. For MongoDB that means:
Capturing application-consistent point-in-time snapshots of an eventually consistent, replicated and distributed database
Establishing continuous backup, even after MongoDB node failure and replica-set master node switchover
Deduplicating different backup copies taken across replica-set nodes, as the physical layout of data across replica nodes is completely different
Leveraging MongoDB’s ability to seamlessly change cluster topology, despite the challenge of restoring earlier backups from old topologies
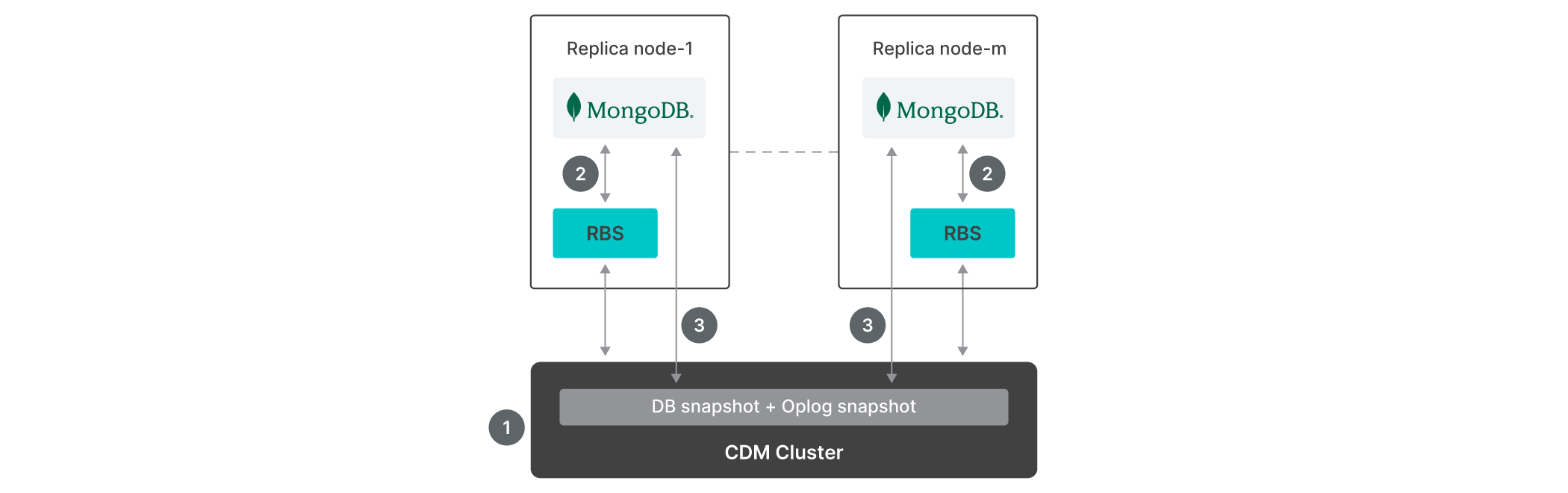
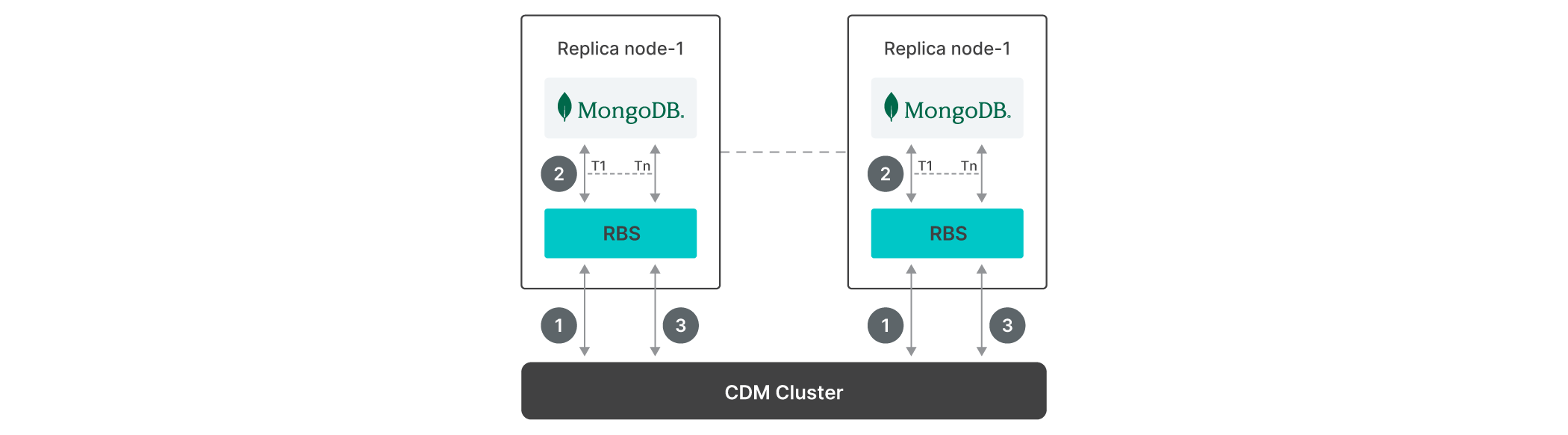
Rubrik can meet these challenges, providing forever incremental and application-consistent backup using MongoDB replication operations logs (oplogs). Oplogs are structured BSON documents that record a history of all write operations performed on the MongoDB database. Here’s how it works:
One time first full backup is taken to create a base backup image.
The incremental merge of oplogs is performed on the base backup image to create the backup image chain.
MongoDB database collections are processed in parallel to speed up the creation of the backup image.